MKV Point is becoming a popular term among those who frequently work with multimedia files. Whether you're a casual viewer or a professional editor, understanding MKV files is essential in today's digital age. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about MKV Point, from its definition and benefits to its usage and compatibility across devices. Let's dive into the world of MKV files and discover why they have become a preferred format for video and audio storage.
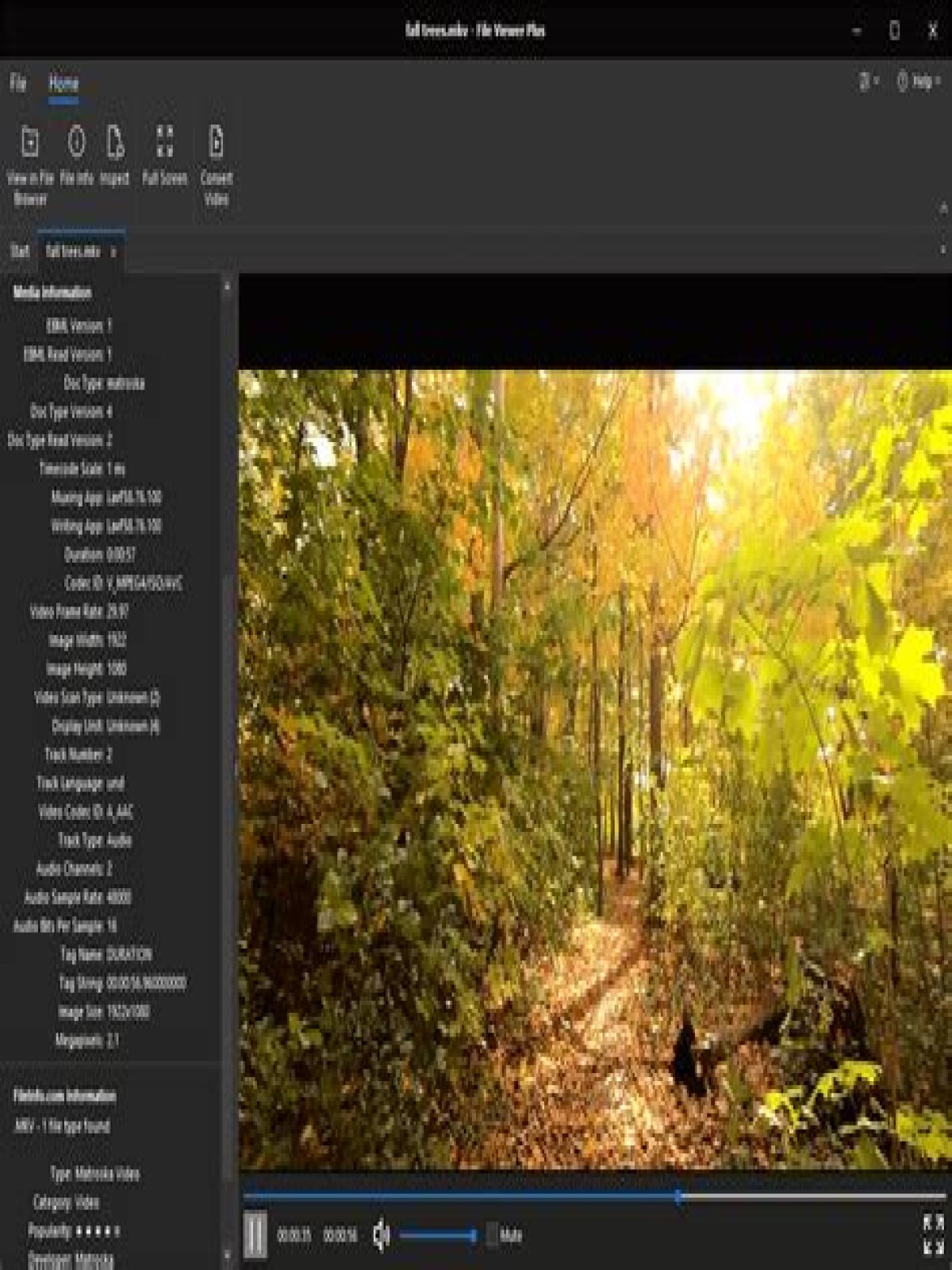
MKV, or Matroska Video, is an open-source multimedia container format that can hold an unlimited number of video, audio, subtitle tracks, and metadata into a single file. Its versatility makes it an ideal choice for various applications, including streaming, downloading, and archiving videos. As the demand for high-quality video content increases, understanding MKV Point will help you navigate this complex landscape more effectively.
This guide aims to provide a thorough understanding of MKV Point, its features, advantages, and how to use it effectively. By the end of this article, you will have the knowledge to make informed decisions about utilizing MKV files for your multimedia projects.
Table of Contents
What is MKV?
Matroska Video, commonly known as MKV, is a free and open-source multimedia container format. It was developed in 2002 by the Matroska team, aiming to create a universal format for storing video, audio, subtitles, and other data. The MKV format can support an unlimited number of tracks, enabling it to store multiple audio languages and subtitle options in a single file.
Key Characteristics of MKV
- Open-source and free to use
- Supports various codecs
- Can include chapters, metadata, and menus
- Compatible with many devices and media players
Features of MKV Files
MKV files come with a range of features that set them apart from other multimedia formats. Some of the notable features include:
- Multiple Tracks: MKV files can contain several audio, video, and subtitle tracks, allowing for a versatile viewing experience.
- High Quality: MKV supports high-definition video and lossless audio quality, making it suitable for high-quality streaming.
- Chapters and Metadata: Users can include chapters and detailed metadata, improving navigation and organization.
- Compatibility: MKV files are compatible with various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and smart TVs.
Benefits of Using MKV Files
The MKV format offers several advantages for both casual users and professionals:
- Flexibility: MKV can store multiple formats of audio and video, making it an all-in-one solution.
- High Compatibility: Many modern media players, including VLC and MPC-HC, support MKV playback.
- Lossless Quality: MKV can maintain the original quality of the video and audio, providing a superior experience.
- Open Source: Being an open-source format, MKV is continuously updated and improved by the community.
How to Play MKV Files
Playing MKV files is straightforward, as numerous media players support this format. Here are some popular options:
- VLC Media Player: A free, open-source media player that plays almost any video format, including MKV.
- Media Player Classic - Home Cinema (MPC-HC): A lightweight media player for Windows that supports MKV files.
- KMPlayer: A versatile media player that supports a wide range of formats, including MKV.
MKV Converters: What You Need to Know
If you need to convert MKV files to another format, several converters can help:
- HandBrake: A popular, open-source video transcoder that can convert MKV files to various formats.
- Freemake Video Converter: A user-friendly converter that supports MKV and can convert to multiple formats.
- Any Video Converter: A versatile tool that allows for quick conversion between different video formats.
MKV vs. Other Formats
While MKV is a powerful format, it is essential to understand how it compares to other popular formats:
MKV vs. MP4
- MP4: More widely supported across devices but has limitations on the number of audio and subtitle tracks.
- MKV: Better for high-quality video and supports multiple tracks.
MKV vs. AVI
- AVI: Older format with less compression, leading to larger file sizes.
- MKV: More modern with better compression and support for more features.
Common Issues with MKV Files
Despite its advantages, users may encounter some issues when working with MKV files:
- Playback Problems: Some devices may not support MKV playback.
- Corrupted Files: MKV files can become corrupted during downloads, leading to playback errors.
- File Size: MKV files can be large, requiring more storage space.
The Future of MKV Files
The MKV format continues to evolve with technology. As streaming services and high-definition content become more prevalent, MKV's features and benefits will likely ensure its relevance in the multimedia landscape. Its open-source nature allows for constant improvements, making it a format worth considering for future projects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding MKV Point is essential for anyone involved in video production or consumption. MKV files offer numerous advantages, including flexibility, high quality, and compatibility with various devices. By leveraging the information in this guide, you can make informed decisions about how to use and manage MKV files effectively.
If you found this article helpful, please leave a comment, share it with your friends, or explore more articles on our site for additional insights.
Penutup
Thank you for reading! We hope this guide has provided you with valuable information about MKV Point. Stay tuned for more articles on multimedia formats and technologies. We look forward to seeing you again!
Hisashi Ouchi: The Tragic Story Behind The Real Photos And Google SearchesBrooke Brandt: A Rising Star In The Entertainment IndustryMolly Noblitt: A Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry